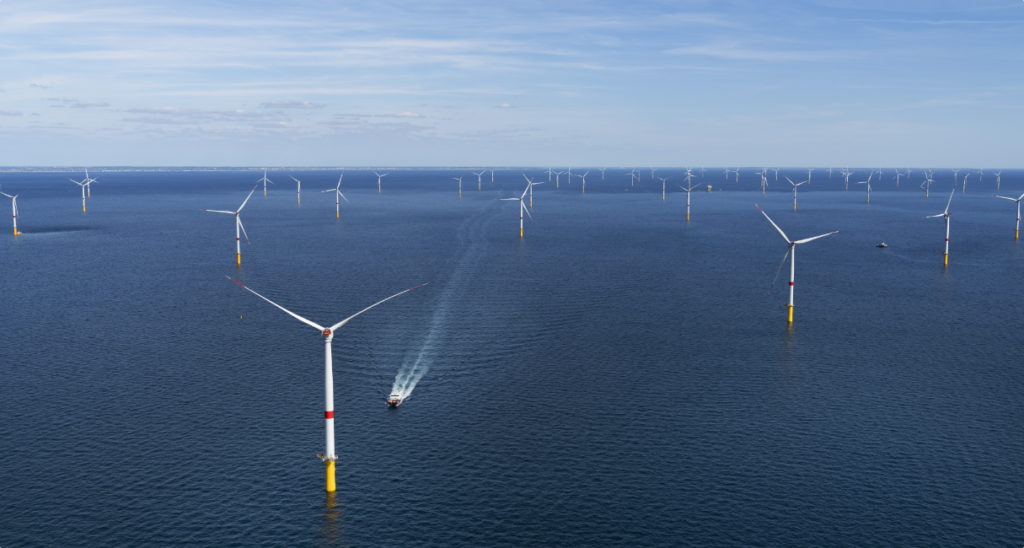
Installed in the open sea, several kilometers from the coast, offshore wind turbines produce electricity using sea winds, which are more powerful and regular than land winds.




THE wind turbines, whether on land or at sea, produce electricity when the wind blows between 10 and 90 km/h. The wind drives the blades of the wind turbine which turn a generator to produce electricity. It's the same operation as a bicycle dynamo!
When the wind picks up, the basket (1) of the wind turbine faces the wind and the blades (2) gradually begin to rotate. The rotor (3) drives the generator (4) which transforms wind energy into electricity.
To ensure the transport of the electricity produced, the wind turbines are connected to each other by underwater cables. (5) and connected to an electrical station installed at sea (6). This station is itself connected to the public electricity network by first submarine cables (7) then underground (8).
The Saint-Nazaire offshore wind farm is made up of 80 wind turbines with a total power of 480 MW. It can produce the equivalent of the electricity consumption of 700,000 people each year.
After several years of technical and environmental studies, the time comes for the work.
Generally planned from early spring until autumn, depending on weather conditions, the installation work is spread out in stages (electrical substation, foundations, cables, wind turbines) over an average duration of 3 years.

Today, the majority of offshore wind turbines rest on foundations firmly installed in or on the seabed, we are talking about “installed” offshore wind farms !
With this technology, we can install wind turbines at sea up to 50 to 60 meters deep!
It is a large steel tube deeply anchored in the seabed.
In the same way as a parasol firmly planted in the sand, it ensures the stability of the wind turbine.
It is a large steel trellis, a sort of large stool, firmly anchored in the sea floor.
Its different feet (three or four depending on the technology) ensure perfect stability.
It is a large concrete structure placed directly on the seabed and then ballasted.
The total weight of the structure, several thousand tons, ensures the stability of the wind turbine.
Impressive and majestic, offshore wind turbines arouse curiosity!
Even if climbing to the top of an offshore wind turbine is strictly reserved for our maintenance technicians, we invite you to discover the behind-the-scenes of an offshore wind farm on video!
If the sea seems to be an immense space of freedom, it is also the place of numerous human activities (fishing, commercial navigation, pleasure craft, etc.) and a place with unique biodiversity which must be preserved!
We cannot therefore install wind turbines at sea just anywhere, but we are rather looking for areas that allow us to reconcile respect for existing activities and the environment.
👉 The three families of criteria to respect when choosing an area to install an offshore wind farm 🌊
The area must have a powerful and regular wind and be sufficiently far from the coast. For installed offshore wind farms, the water depth should not exceed 50 to 60 meters.
The installation of wind turbines must be compatible with the biodiversity of the site. In-depth studies are carried out by experts to understand the environmental issues in the area and adapt the project accordingly. Taking the environment into account is an obligation which is subject to strict supervision and control by State services.
Wind turbines must not disrupt existing activities, such as commercial fishing or commercial shipping. Offshore wind projects are being developed in consultation with communities, fishermen and other sea users in the area concerned.
For each offshore wind project, broad consultation is set up with residents, boaters, fishermen and all sea users. These numerous meetings make it possible to better understand the needs of each person and to integrate a maximum opinions and proposals in the definition of the project.
Additionally, a monitoring of fishery resources (i.e. monitoring of the fish population), is set up in order to compare the presence of fish before and after the installation of the wind turbines.
Even though wind turbines are generally located between 10 and 25 km from the coast, they are visible from the beach. If we want to produce carbon-free and abundant electricity using the renewable energies available to us such as wind, it is necessary to install wind turbines at sea! However, we are working on several ways to reduce the visual impact, such as aligning the wind turbines from the most notable viewpoints on the coast.
An offshore wind farm is big! The wind turbines are generally one kilometer apart, which allows boats to continue to navigate within the park, provided they respect safety rules!
We explain to you
Before installing an offshore wind farm, we take the time to carry out a whole series of environmental studies.
the biodiversity of the site is studied, whether underwater (marine mammals, fish, crustaceans, etc.), or aerial (birds, bats, etc.), as well as other environmental factors such as sea currents and nature of the ground.
The objective is to fully know and understand the environmental issues of the site in order to be able to size and best integrate the park into the natural environment!
Response from EDF Renewables:
First of all, you should know that once put into service, the noise generated by an offshore wind farm is very low and is not capable of disturbing marine mammals such as whales. However, discomfort is possible during the foundation installation phase. This phase is, however, very short, of the order of a few hours per foundation, and we are putting in place specific measures such as the detection of the most sensitive species (scaring system) and a gradual start of the noisiest operations.
Once installed, the foundations of wind turbines are quickly colonized by algae, mussels and micro-organisms, thus attracting crustaceans and fish which will come and feed there… This is what we call the reef effect. !
An offshore wind farm doesn’t just produce renewable, carbon-free energy. Jobs linked to the construction or maintenance of wind turbines, economic benefits for communities and industrial tourism. An offshore wind farm also has many positive benefits for the region where it is located!
 Jobs in the wind!
Jobs in the wind!In France, the Marine Renewable Energy sector employs more than 7,500 jobs at the end of 2022. A figure up 141TP3Q compared to the previous year.
These jobs are mainly located in the regions hosting projects. Thus, 60% of these jobs are located in the Normandy and Pays de la Loire Regions.
For several years, we have indeed witnessed the emergence of a French industrial sector of excellence in offshore wind power with the establishment of wind turbine manufacturing plants in major French ports such as Saint-Nazaire, Le Havre or even Cherbourg.
In addition, each offshore wind farm requires the creation of a maintenance base in the immediate vicinity of the park, thus creating around a hundred long-term jobs such as maintenance technicians, engineers, logisticians…
 Benefits for communities
Benefits for communities Each offshore wind farm is subject to a special tax, called the “Maritime Wind Turbine Tax”, levied by the tax services and paid to local authorities to finance local projects.. This tax depends on the power of the wind farm, it is then distributed as follows:
For the Saint-Nazaire offshore wind farm, this tax represents a total amount of 9 million euros each year.
An offshore wind farm can also generate curiosity. We thus see the development of dedicated sea trips for tourists or locals, this is what we call industrial tourism!
Of course ! It is entirely possible to board a tourist boat to visit an offshore wind farm. With a little luck, you will even come across dolphins there.
Find out more at the tourist office closest to the offshore wind farm or otherwise go to the site visit page on our website !
 Focus
Focus 
Working at the top of a wind turbine located in the open sea, more than 10 km from the coast, cannot be improvised! We take you to discover the story of Nicolas in his journey to work on the first French offshore wind farm, off the coast of Saint-Nazaire 
 What if we made wind turbines float?
What if we made wind turbines float?To install offshore wind turbines where the water depth exceeds 50 meters, a new technology is emerging: floating offshore wind power.
The principle is simple, the wind turbine this time rests on a giant float, firmly anchored to the seabed by anchor lines. With this technique, it is possible to capture sea winds where they are, in water depths that can exceed 100 meters!
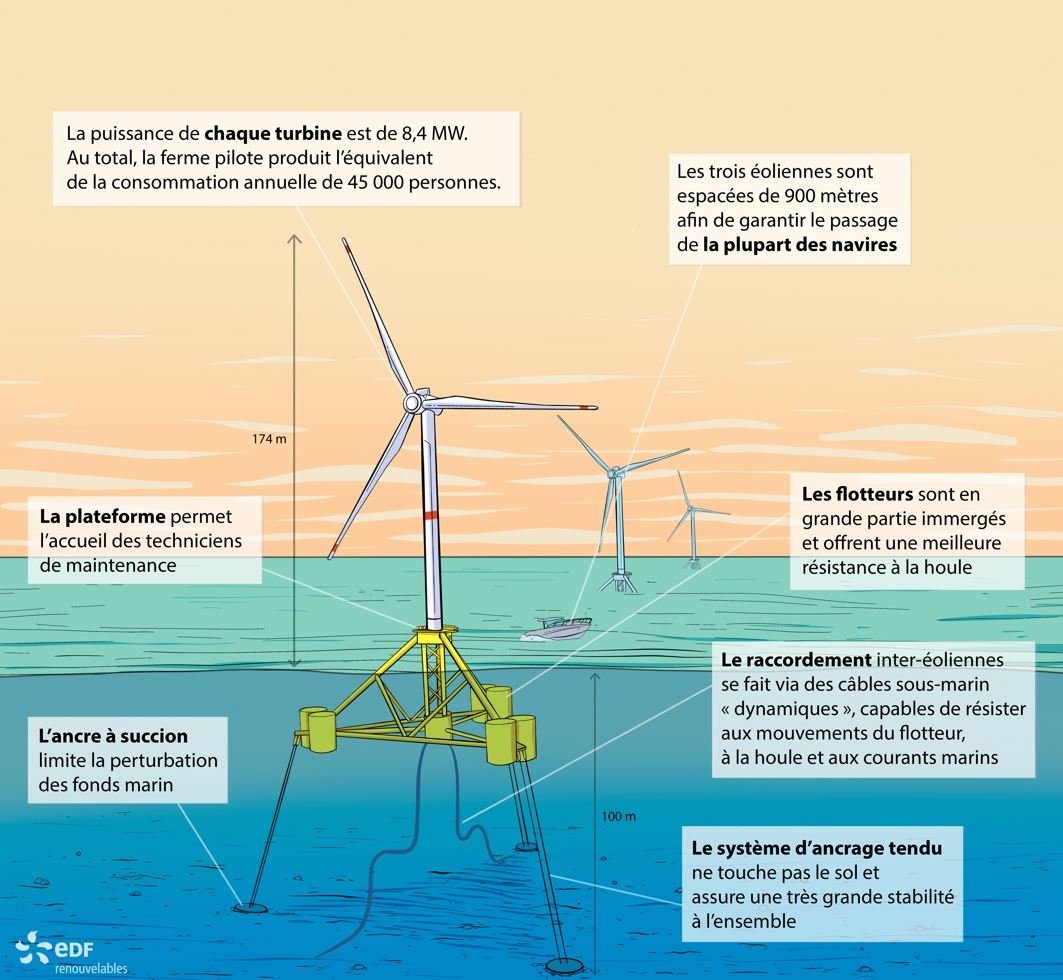
Installed in 2023 more than 17 km from the coast, in an area where the depth exceeds 100 meters, the 3 wind turbines of the “Provence Grand Large” project aim to collect complete feedback on this new technology and to accelerate the development of the sector!
Marine Renewable Energy: These are energy sources produced from marine resources, such as waves, sea wind, tides, ocean currents, temperature difference between sea water and air. These energy sources are renewable because they are constantly present and do not run out. Technologies used to harness these renewable marine energies include tidal turbines (using ocean currents), wave converters (using wave energy), tidal plants (using tidal energy) and offshore wind turbines (using sea winds). Marine renewable energies offer significant potential for diversifying the energy mix.
Industrial tourism: It is a form of tourism focused on visiting businesses, factories or industrial sites. It allows visitors to discover the manufacturing processes, the technologies used and behind the scenes of the industries. Tourists can observe the different stages of production, interact with the workers. Industrial tourism offers a unique perspective on the world of work and provides a better understanding of the economic activities of a region or country. It can also contribute to local development by attracting visitors and stimulating the regional economy.
Marine biodiversity: Marine biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms present in marine ecosystems. It encompasses a great diversity of animal and plant species, as well as the habitats and marine ecosystems in which they live. Marine biodiversity is essential for maintaining the ecological balance of the oceans and providing ecosystem services such as oxygen production, climate regulation, water filtration, and the provision of food and economic resources for human communities.
Jack-up ship: It is a type of vessel used in the offshore industry for offshore drilling, construction or heavy maintenance operations. It is fitted with telescopic legs (or "jacks") which can be lowered to the seabed to stabilize the vessel and keep it in position during the work. This allows the vessel to work in shallow waters or in areas where the construction of fixed infrastructure is not possible. Jack-up vessels are often used for installing offshore wind turbines, constructing oil or gas platforms, and other offshore engineering projects.
Find all the resources available on this theme in the media library
43 Boulevard des Bouvets
CS 90310
92741 NANTERRE CEDEX
©2025 EDF Renewables