Everyone talks about renewable energies and everyone has their opinion! If they are considered one of the three essential pillars for a successful Energy Transition, their rapid growth in recent years arouses curiosity, we explain!




We might think that in France, nuclear power plants are sufficient to produce electricity that is already largely low-carbon and that we do not need new means of production. This would confuse energy mix and electricity mix!
If our electricity is largely low-carbon (thanks to nuclear power and renewable energies), this is not the case for all of the energy we consume every day to move around, heat ourselves, cook, etc.
Thus, in France, still 66% of the energy consumed comes from fossil fuels!
To achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, we must therefore significantly reduce the place of fossil fuels (oil, gas, fuel oil, etc.) in our energy mix, and develop low-carbon energies.
Electricity offers a tremendous opportunity because we know how to produce it in different ways.
The production of electricity using coal or gas emits very high amounts of CO2. However, this is not the case for all means of production.
Thus, it is entirely possible to produce electricity while emitting little CO2, for example by usingreading nuclear or renewable energies (hydraulic dams, wind turbines or solar panels, etc.).
There are 5 main families of renewable energies: wind energy (land and sea), solar energy (photovoltaic and thermal), the biomass (wood energy), hydraulic energy And geothermal energy. They are called renewable because they come from nature, do not run out and emit very few greenhouse gases.
Every day, EDF Renewables teams develop, build and operate wind (onshore and offshore) and solar projects all over the world, contributing to the development of low-carbon means of electricity production.
 Low carbon energy day and night, with or without wind!
Low carbon energy day and night, with or without wind!Renewable energies use natural resources such as wind, sun or water to produce electricity. It is therefore normal that production depends on their availability.
But since we need energy day and night, whether there is wind or not, we must design a suitable electrical system. Anticipation of production several days in advance, development of storage means, interconnection of the network at European level but above all complementary electricity mix, we take stock of the way in which the electricity network is organized to be operational 24/7!
Throughout the world, the need to reconcile energy needs, reduction of CO2 emissions and the fight against climate change has led to a strong development of renewable energies.
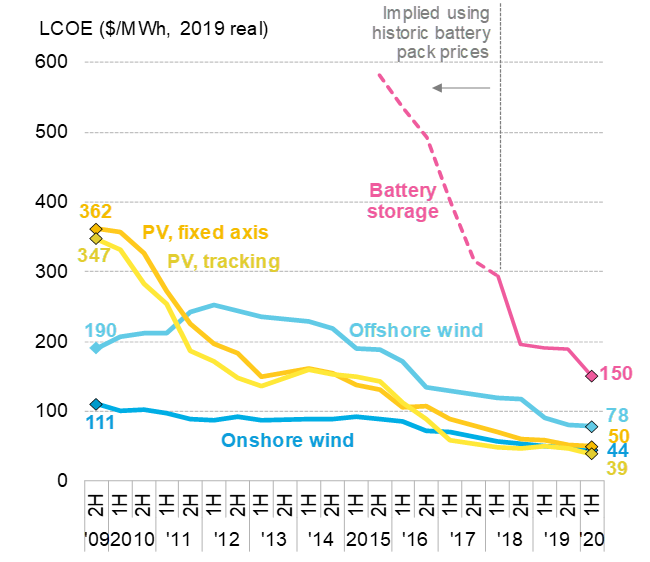
Still emerging around twenty years ago, the rapid development of renewables has led to a spectacular drop in costs. Thus, in the space of 10 years, the cost of producing solar energy has been divided by 7 and that of offshore wind power has been divided by 2.5.
Worldwide, installed renewable energy capacity is growing by nearly 20% per year!
In France, renewable energies are also a highly job-creating sector.
Whether it is developing projects, building components such as wind turbines or ensuring daily maintenance of equipment, employment in the renewables sector is growing strongly.
In France, the wind industry alone represents more than 28,000 direct and indirect jobs.

In France, the first factory dedicated to the assembly of offshore wind turbines was inaugurated in 2016 in Saint-Nazaire by General Electric. An offshore wind turbine blade factory has also emerged in Cherbourg. Finally, it is in Le Havre that Siemens-Gamesa commissioned a factory dedicated to offshore wind power in 2022. The latter employs more than 700 people.
Energy mix : The energy mix refers to the combination of different energy sources used to meet the needs of a region or country. It includes energy sources such as oil, natural gas, coal, nuclear power, hydropower, wind power, solar power, etc. The energy mix can vary from one location to another depending on available resources, energy policies and environmental concerns. The objective is often to diversify the energy mix in order to guarantee a reliable, sustainable and environmentally friendly supply.
Electric energy : Electrical energy is a form of energy widely used in our daily lives. It is generated by the flow of electrons through conductors, such as electrical wires. This energy is essential for powering electrical appliances, turning on lights, running computers and much more. It is produced in power plants and transported to our homes through electricity distribution networks.
Energetic transition : Energy transition refers to the process of moving from an energy system historically based on fossil fuels (such as oil, natural gas and coal) to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly system. The main objective is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. The energy transition also requires a reduction in our energy consumption and better energy efficiency. The aim is to ensure a secure, clean and sustainable energy supply for present and future generations.
Climate change : Refers to long-term changes in Earth's climatic conditions. It is mainly caused by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, resulting from human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels. These gases trap heat from the sun, causing an increase in the planet's average temperature, changes in precipitation patterns, variations in temperature extremes, and other significant climate changes. Climate change has impacts on ecosystems, water resources, agriculture, human health and biodiversity.
Find all the resources available on this theme in the media library
43 Boulevard des Bouvets
CS 90310
92741 NANTERRE CEDEX
©2025 EDF Renewables